In an age where digital privacy is becoming increasingly elusive, understanding the entities that monitor and share our online activities is crucial. One such entity is the Nine Eyes Alliance, a powerful coalition of countries that collaborates on intelligence and surveillance.
For VPN users, this alliance has significant implications for privacy, security, and functionality. So, this article delves into the Nine Eyes Alliance, its impact on VPN users, and strategies to mitigate associated risks.
Brief Overview of the Nine Eyes Alliance
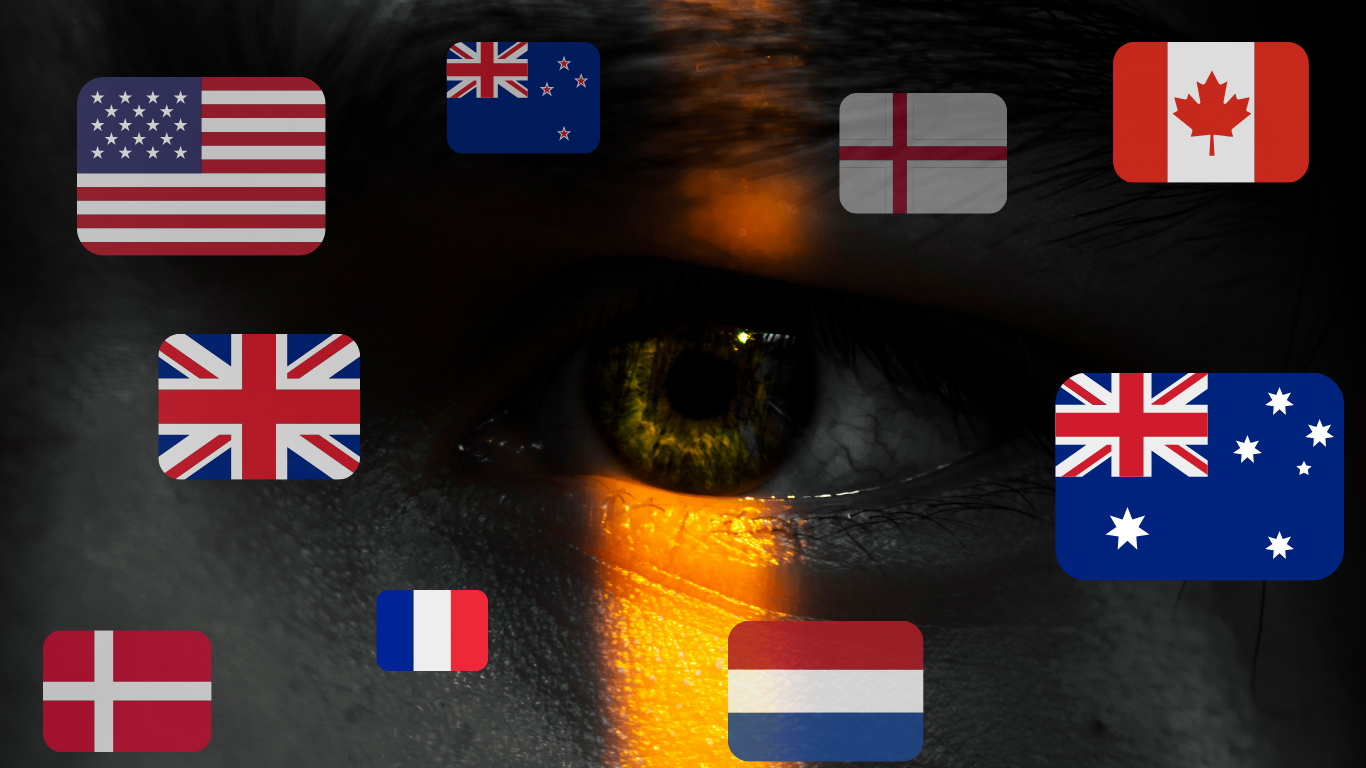
The Nine Eyes Alliance is an expansion of the original Five Eyes Alliance, which consists of the United States, the United Kingdom, Canada, Australia, and New Zealand. The Nine Eyes extends this coalition to include Denmark, France, the Netherlands, and Norway. This alliance aims to enhance intelligence sharing and collaborative security efforts among member countries, posing both benefits and challenges for internet users worldwide.
Understanding the Nine Eyes is vital for VPN users. This alliance’s surveillance capabilities mean that online activities might be monitored and shared among member countries, potentially compromising the privacy that VPN users seek. Knowing how this alliance operates helps users make informed decisions about their online security.
What is The Nine Eyes Alliance?
Definition and Purpose of the Alliance
The Nine Eyes Alliance is a collective intelligence-sharing agreement between nine countries. Its primary purpose is to enhance global security through the collaborative gathering, sharing, and analyzing of intelligence data. By pooling resources and information, these countries aim to combat global threats more effectively.
Member Countries of The Nine Eyes Alliance
The alliance includes the United States, the United Kingdom, Canada, Australia, New Zealand, Denmark, France, the Netherlands, and Norway. Each member country contributes to and benefits from the shared intelligence, making the alliance a formidable force in global surveillance.
History and Formation of the Alliance
The Nine Eyes Alliance evolved from the original Five Eyes Alliance, established during World War II. The expansion to Nine Eyes occurred to address the growing need for broader intelligence sharing in response to global security threats. This evolution highlights the increasing complexity and reach of international surveillance efforts.
How Does the Nine Eyes Alliance Work?
- Intelligence Sharing and Collaboration
The core function of the Nine Eyes Alliance is the exchange of intelligence between member countries. This involves sharing data collected through various means, including electronic surveillance, human intelligence, and signals intelligence. The collaborative nature ensures that each country has access to a broader pool of information.
- Joint Operations
Member countries often engage in joint operations to gather intelligence and combat global threats. These operations may involve cyber surveillance, counter-terrorism efforts, and monitoring of international communications. The coordination between countries enhances the effectiveness of these operations.
- Impact on Global Security
The Nine Eyes Alliance significantly impacts global security by providing member countries with enhanced capabilities to detect and respond to threats. However, this extensive surveillance network also raises concerns about privacy and the potential for abuse of power.

The Nine Eyes Alliance’s Impact on VPN Users
- Increased Scrutiny of VPN Providers
VPN providers operating in Nine Eyes countries face unique challenges due to the increased scrutiny and data retention requirements imposed by these governments. However, some providers have managed to navigate these hurdles and continue to offer reliable services.
When choosing a VPN provider operating in a Nine Eyes country, it’s essential to consider the following factors:
- Privacy Policy: Ensure the provider has a strong privacy policy that clearly outlines its commitment to protecting user data.
- No-Logs Policy: Look for providers that adhere to a strict no-logs policy, meaning they don’t store any user data that could be used to identify them.
- Jurisdiction: Consider the provider’s jurisdiction. While operating in a Nine Eyes country might pose risks, some jurisdictions may have stronger privacy protections than others.
- Security Features: Evaluate the provider’s security features, such as multi-hop connections, kill switches, and encryption protocols.
Here are some examples of VPN providers operating in Nine Eyes countries:
- NordVPN: While headquartered in Panama, NordVPN has servers in many Nine Eyes countries. It offers a strong privacy policy and a no-logs policy.
- ExpressVPN: Based in the British Virgin Islands, ExpressVPN operates servers in Nine Eyes countries. It has a strict no-logs policy and offers advanced security features.
- CyberGhost: This Romanian-based provider has servers in Nine Eyes countries. It offers a no-logs policy and a user-friendly interface.
It’s important to note that even VPN providers operating in Nine Eyes countries may face challenges. Governments can still request user data or impose restrictions on VPN services. Therefore, it’s crucial to research and choose a provider that aligns with your privacy needs and is committed to protecting your data.
- Data Retention Requirements
The Nine Eyes Alliance countries have varying data retention laws that can significantly impact VPN providers operating within their jurisdictions. These laws often require ISPs and VPN providers to store user data for a specific period, which can compromise user privacy.
Key Data Retention Requirements in Nine Eyes Countries:
- United States: While there isn’t a federal mandate for general data retention, individual states have varying laws. For example, California’s Electronic Communications Privacy Act (ECPA) requires certain electronic communications records to be retained for up to 180 days.
- United Kingdom: The Investigatory Powers Act (IPA) requires ISPs to retain certain communications data for up to 12 months.
- Canada: The Personal Information Protection and Electronic Documents Act (PIPEDA) doesn’t explicitly mandate data retention for VPN providers, but it does require organizations to collect, use, and disclose personal information in a responsible manner.
- Australia: The Telecommunications Act 1997 requires carriage service providers, including VPN providers, to retain certain metadata for a period of two years.
- New Zealand: The Privacy Act 2020 doesn’t have specific data retention requirements for VPN providers, but it does require organizations to collect, use, and disclose personal information in a responsible manner.
Implications for VPN Users:
- Increased Risk of Surveillance: Data retention laws can increase the risk of government surveillance, as authorities may be able to access and analyze user data.
- Limited Privacy: The retention of user data can limit the effectiveness of VPNs in protecting privacy, as governments may be able to track user activity over time.
- Legal Challenges: VPN providers may face legal challenges if they fail to comply with data retention laws.
Strategies for VPN Users:
- Choose a Provider with a Strong Privacy Policy: Look for providers that have a clear commitment to protecting user privacy and resisting government requests for data.
- Consider Offshore Providers: VPN providers based outside of Nine Eyes countries may offer greater privacy protections.
- Use Advanced Security Features: Look for providers that offer features like multi-hop connections, kill switches, and strong encryption protocols.
- Stay Informed: Keep up-to-date on data retention laws in the countries where you use VPN services.
By understanding the data retention requirements in Nine Eyes countries and taking proactive steps to protect your privacy, you can mitigate the risks associated with using VPNs in these jurisdictions.
Governments in Nine Eyes countries may interfere with VPN services, either by imposing restrictions or demanding access to user data. This interference can reduce the effectiveness of VPNs in protecting user privacy.
The extensive surveillance capabilities of the Nine Eyes Alliance mean that VPN users in member countries may experience reduced privacy. While VPNs encrypt data, the metadata and other identifying information may still be accessible to surveillance agencies.
Limited Functionality of VPNs
Government actions, such as blocking certain VPN protocols or imposing restrictions on VPN usage, can limit the functionality of VPNs. This can hinder users’ ability to bypass censorship or access geo-restricted content.
- Blocking: Governments may block VPN services or specific VPN servers to limit their citizens’ access to the internet or certain content.
- Deep Packet Inspection (DPI): Authorities can use DPI to identify and block VPN traffic, even if it’s encrypted.
- Metadata Collection: As discussed earlier, data retention laws require VPN providers to store certain metadata, which can be used to track user activity over time.
- Forced Disclosure: Governments may compel VPN providers to disclose user data based on legal requests or court orders.
- Physical Access: In some cases, governments may seize VPN servers located within their jurisdictions, disrupting service and potentially compromising user data.
Legal Risks for VPN Users
In some Nine Eyes countries, using a VPN for certain activities may carry legal risks. Users must be aware of the laws and regulations in their country to avoid potential legal repercussions.
How to Stay Hidden Under the Nine Eyes Alliances?
The Nine Eyes Alliance poses significant challenges for VPN users seeking to protect their privacy. To effectively navigate this landscape, it’s crucial to select a reputable VPN provider. Here’s a guide to help you make an informed decision:
- Choose Reputable VPN Providers
Opt for VPN providers with a strong reputation for privacy and security. Research their privacy policies, logging practices, and history of compliance with government demands. Providers with a proven track record of protecting user data are preferable. Some key factors to consider for the best VPN to stay hidden from the 9 eyes include:
- Outside Nine Eyes: Opt for providers based in countries outside the Nine Eyes Alliance, such as the British Virgin Islands, Panama, or Switzerland. These jurisdictions often have stronger privacy laws and are less likely to cooperate with data requests from Nine Eyes members.
- Strict Adherence to No-Logs Policy: Ensure the provider has a strict no-logs policy, meaning they don’t store any personally identifiable information about your online activities. This prevents governments from accessing your data even if they request it.
- Robust Encryption: Look for providers that use strong encryption protocols like OpenVPN, WireGuard, or IKEv2/IPsec. These protocols help to protect your data from being intercepted and decrypted.
- Kill Switch & Data Protection: A kill switch is a crucial feature that automatically disconnects your internet connection if the VPN fails, preventing your data from being exposed.
- Global Server Coverage: A provider with a vast global server network offers more options for bypassing censorship and improving connection speeds.
- Consider Offshore VPN Providers
Using VPN providers based in countries outside the Nine Eyes Alliance can help mitigate the risk of government interference. These providers are not subject to the same surveillance agreements and may offer better protection for user privacy.
- Use Advanced Security Features
Leverage advanced security features offered by VPN providers, such as multi-hop connections, obfuscation techniques, and strong encryption protocols. These features enhance privacy and make it more difficult for surveillance agencies to track online activities.
- Stay Informed About Privacy Laws and Regulations
Understanding the legal landscape is crucial for protecting your privacy in the digital age. While the Nine Eyes Alliance can pose significant threats to online privacy, staying informed about the relevant laws and regulations can help you stay hidden. Here are some key privacy laws and regulations in Nine Eyes countries you can focus on:
- General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR): Although not specifically part of the Nine Eyes Alliance, the GDPR is a landmark piece of European Union legislation that has significant implications for data privacy. It gives individuals more control over their personal data and imposes strict obligations on organizations that handle that data.
- California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA): This California law grants consumers certain rights regarding their personal information, including the right to know what data is collected, the right to delete data, and the right to opt-out of the sale of personal information.
- Privacy Act 2020 (New Zealand): This New Zealand law provides individuals with the right to access and correct their personal information, as well as the right to complain to the Privacy Commissioner.
- Data Protection Act 2018 (United Kingdom): This UK law sets out the data protection rights of individuals and imposes obligations on organizations that handle personal data.
Case Study: Government Actions Against VPN Providers
Examining case studies of government actions against VPN providers can provide insights into the risks and help users identify which providers are more resilient to government pressure. This knowledge aids in selecting a reliable VPN service. The Nine Eyes Alliance has a history of taking actions against VPN providers, often citing national security concerns or legal violations. Here are a few notable case studies:
1. Australia’s Crackdown on VPNs
- Reason: In 2018, Australia’s Home Affairs Department launched a crackdown on VPN providers that were allegedly helping Australians access blocked content, such as online gambling websites.
- Action: The government threatened legal action against VPN providers and pressured internet service providers (ISPs) to block access to certain VPN servers.

2. United States’ Surveillance of VPN Users
- Reason: The US government has been accused of using mass surveillance programs to monitor VPN users, particularly those suspected of terrorism or other criminal activities.
- Action: US intelligence agencies have been reported to have used techniques like deep packet inspection to identify and intercept VPN traffic.
3. UK’s Data Retention Laws and VPNs
- Reason: The UK’s Investigatory Powers Act (IPA) requires ISPs to retain certain communications data, including metadata from VPN connections.
- Action: While the IPA doesn’t specifically target VPN providers, it can be used to obtain information about VPN users if authorities suspect illegal activity.
4. Canada’s Law Enforcement Requests
- Reason: Canadian law enforcement agencies have been known to issue warrants to compel VPN providers to disclose user data.
- Action: These requests can be based on national security concerns or investigations into criminal activities.
It’s important to note that these are just a few examples, and the actions taken by Nine Eyes governments against VPN providers can vary widely. Factors such as the specific country, the nature of the alleged violation, and the political climate can influence the government’s response.
Future of the Nine Eyes Alliance
As global security threats evolve, the Nine Eyes Alliance will likely continue to expand its surveillance capabilities. This expansion poses ongoing challenges for VPN users seeking privacy and anonymity online. Staying informed about these developments and adapting strategies accordingly is essential for maintaining online privacy.
The Nine Eyes Alliance is likely to remain a significant force in global security. As technology evolves and new threats emerge, the alliance may expand its membership, enhance collaboration, and adopt new technologies to counter emerging threats. However, growing public concerns about privacy and surveillance could lead to increased scrutiny of the alliance’s activities and potential legal challenges.
For VPN users, the future outlook is uncertain. While the alliance may continue to pose challenges, technological advancements and evolving legal frameworks could offer opportunities for greater privacy protection. Staying informed about the latest developments in privacy laws and regulations, choosing reputable VPN providers, and utilizing advanced security features are essential steps to mitigate the risks associated with operating in the Nine Eyes environment.
Conclusion
Understanding the Nine Eyes Alliance and its implications for VPN users is crucial in the digital age. By choosing reputable VPN providers, leveraging advanced security features, and staying informed about privacy laws, users can take proactive steps to protect their online privacy. As surveillance efforts intensify, maintaining vigilance and adapting to new challenges will be key to staying hidden online.